The meaning of Learning Management System (LMS)
Find out what a Learning Management System is. What does it do? What are the benefits of having LMS, and how to select the best LMS for your organization?

Discover:
- What is a Learning Management System (LMS)?
- Why you need it – What is an LMS used for?
- How you will benefit – Key LMS benefits
- Most important LMS features
- How to find the right (and the best for you) Learning Management System (LMS)
What is a Learning Management System (LMS)?
A learning management system (LMS) is a software that is designed specifically to create, distribute, and manage the delivery of educational content. The LMS can be hosted as a stand-alone product on the company server, or it can be a cloud-based platform that is hosted by the software firm.
Think of a learning management system as technology that can improve learning, make it faster, productive, cost-effective, and what is more important – trackable.
The most basic LMS contains a core functional platform that enables administrators to upload learning content, deliver lessons to employees, serving notifications, and share data with authorized users.
An LMS most often operates inside of a web-browser, behind a secure sign-on process. This gives all learners and instructors easy access to courses on-the-go, while administrators and leaders can monitor learner progress and make improvements.
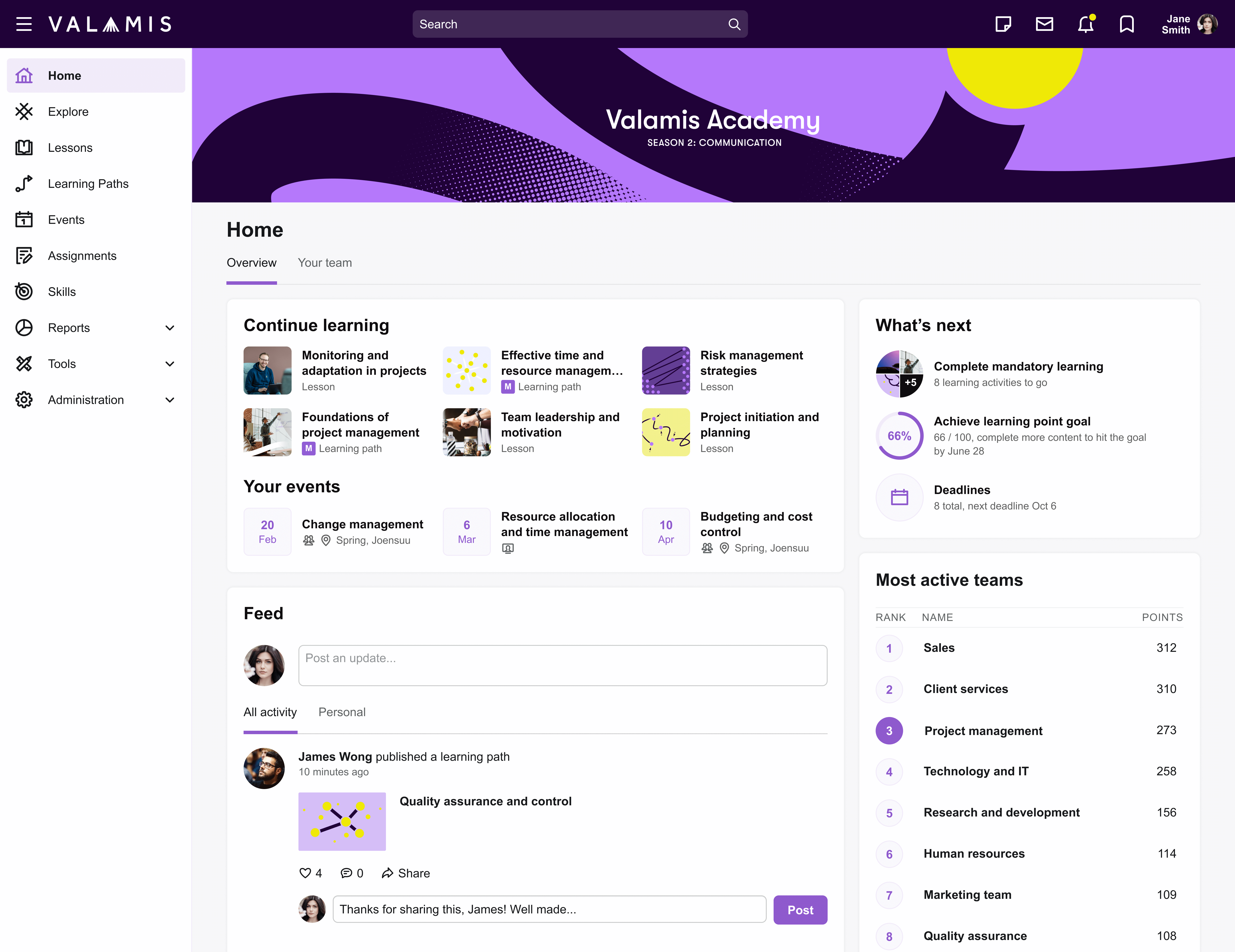
Example of the interface and main page of the Valamis training platform
What is an LMS used for?
Considering the comprehensive range of functions, features, and benefits that Learning Management Systems offer, it is now appropriate to explore specific use cases and applications to understand how an LMS can be effectively employed within your organization.
Each business will have different objectives and reasons for choosing an LMS system for internal training.
There are generally several layers of LMS use within businesses, including: employee onboarding and job training, customer education, and professional leadership development.
All of these areas may approach the use of the LMS in a unique way, with courses and learning content design aimed at each group.
1. LMS for onboarding and orientation
An LMS can be used to deliver onboarding and orientation materials to new employees, familiarizing them with company policies, procedures, and culture.
This helps ensure a smooth and consistent onboarding experience.
2. For skill development and training
LMSs can host a variety of courses and training materials tailored to an organization’s specific needs.
Employees can access these resources to develop their skills, improve their job performance, and stay up-to-date with industry trends and best practices.
3. LMS for compliance training
Organizations often need to provide mandatory compliance training to their employees, such as workplace safety, anti-harassment, and data privacy.
An LMS can help manage and track the completion of these training modules, ensuring all employees meet regulatory requirements.
4. LMS for performance management
Instructors and managers can use the LMS to track employee progress and performance in training programs, identifying areas where employees may need additional support or coaching.
5. LMS for career development
An LMS can be used to support employee career development by offering resources and courses related to specific career paths, enabling employees to acquire new skills and qualifications that support their career growth within the organization.
6. For collaboration and knowledge sharing
An LMS can facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees through discussion forums, chat features, and other communication tools. This helps create a culture of continuous learning and knowledge exchange.
7. LMS for personalized learning
LMSs often include features that allow for personalized learning experiences, such as adaptive learning paths and recommendations based on individual preferences and performance. This ensures that employees can focus on the most relevant and impactful training for their needs.
8. LMS for analytics and reporting
An LMS can provide valuable insights into employee learning and development through analytics and reporting. This data can be used to assess the effectiveness of training programs and make informed decisions about future initiatives.
Watch the video, where Samuel from Valtech, delve into the pivotal role learner data plays in shaping effective and efficient learning cultures.
9. For time and cost savings
By providing a centralized platform for delivering and managing training materials, an LMS can help organizations save time and resources on employee learning and development compared to traditional face-to-face training methods.
10. LMS for remote and mobile access
LMSs that are optimized for mobile devices enable employees to access learning materials from anywhere, at any time, making it easier for them to fit professional development into their schedules.
Implementing an LMS for employee learning and development can lead to a more knowledgeable, skilled, and engaged workforce, ultimately resulting in increased productivity, innovation, and overall organizational success.
Read more: What is the difference between LMS and LXP
Key benefits of having Learning Management Systems (LMSs)
All of early mentioned use cases areas may approach the use of the LMS in a unique way, with courses and learning content design aimed at each group.
As a whole, learning management systems help to streamline learning activities in any organization.
These benefits can significantly enhance employee performance, streamline training processes, and promote a culture of continuous learning and development within the organization.

1. Centralized learning
An LMS provides a centralized platform for managing and delivering training content, making it easy for employees to access the resources they need, and for administrators to manage course materials and track learner progress.
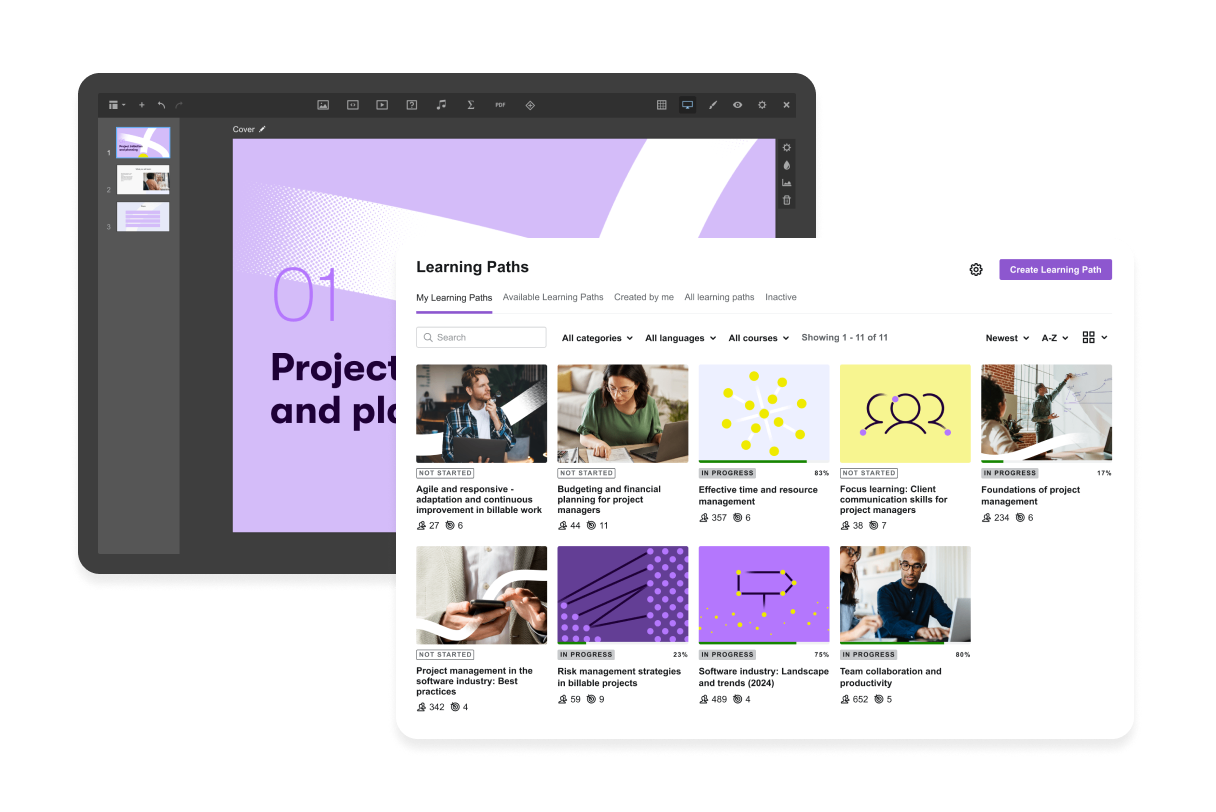
The example of centralized content library at Valamis
2. Cost-effectiveness
Implementing an LMS can help businesses reduce training costs by eliminating the need for printed materials, venue rentals, and instructor fees associated with traditional face-to-face training.
Additionally, it allows for easy updating and modification of training content, reducing the costs of ongoing maintenance.
Read the success story on How to reduce the cost of employee training
3. Time savings
LMS enables employees to learn at their own pace, from anywhere and at any time, reducing the time spent on scheduling and coordinating in-person training sessions.
This flexibility allows employees to engage in training activities without disrupting their regular work schedules.
4. Consistent and standardized training
An LMS ensures that all employees receive consistent and standardized training, regardless of their location or job role.
This helps maintain a high level of quality and compliance across the organization.
5. Personalized learning experiences
LMS software allows for personalized learning paths and content recommendations, ensuring that employees focus on the most relevant and impactful training for their needs.
This tailored approach can lead to better engagement and improved learning outcomes.
6. Tracking and reporting
LMS platforms offer robust tracking and reporting tools that enable businesses to monitor employee progress, assess the effectiveness of training programs, and identify areas for improvement.
These insights can help organizations make informed decisions about their learning and development initiatives.
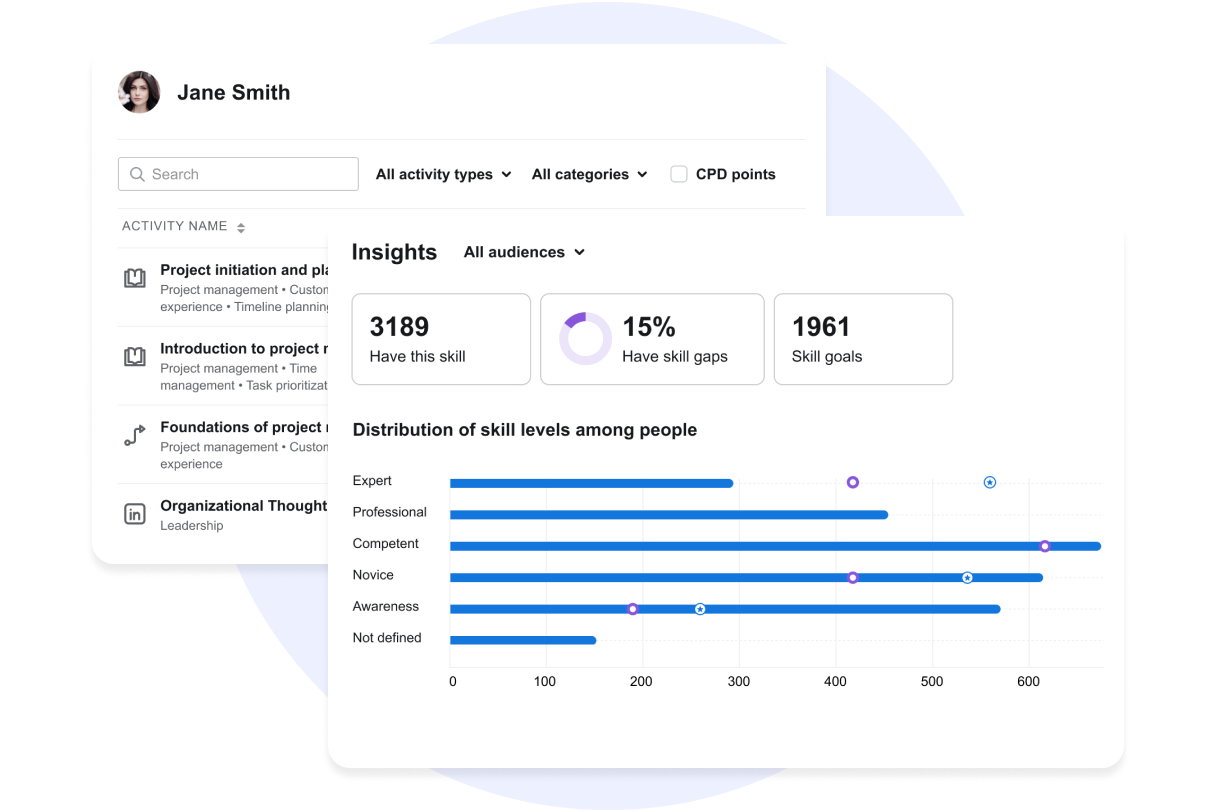
Example of Skills and completions reports at Valamis
7. Improved employee performance and productivity
By providing employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, LMS software can lead to improved job performance and increased productivity.
Well-trained employees are more likely to feel confident in their abilities, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and retention.
8. Regulatory compliance
Many industries require businesses to provide specific training for employees to comply with regulations, such as workplace safety or data protection.
An LMS can help manage and track the completion of these training modules, ensuring all employees meet the necessary requirements.

MadeiraMadeira achieves impressive KPI results in completion rates after implementing new learning platform — read the full story
9. Scalability
LMS software can easily scale to accommodate business growth, making it simple to add new courses, users, or even expand training programs to additional departments or locations.
10. Encouraging a learning culture
Implementing an LMS can help promote a culture of continuous learning and development within the organization.
This fosters a growth mindset among employees, encouraging them to seek out new opportunities for professional growth and skill development.
LMS features
In most cases, organizations use an LMS system to facilitate access to learning materials that range from written materials and presentations to videos and interactive lessons.
Given this broad usage, it’s important to understand the main functions an LMS should offer to effectively support diverse learning and administrative needs.
Here are some of the LMS primary functions and supporting features
The following list should provide a clearer structure of primary LMS functions along with the features that support them.

Keep in mind that different LMS platforms may offer varying sets of features, so it’s essential to evaluate each platform based on your organization’s specific needs and requirements.
1. Course creation and management: The best LMSs allow administrators or instructors to create, edit, and manage course content, including multimedia materials like text, images, videos, and audio.
LMS features:
- Multimedia content support (text, images, videos, audio)
- Course templates
- Content import/export (SCORM, xAPI, IMS Common Cartridge)
- Content organization and categorization
- Course versioning and archiving

The example of Valamis Studio and embedded content creation tools
2. Course delivery: LMSs enable the delivery of online courses, providing employees with access to learning materials and interactive features like quizzes, assignments, and discussion forums.
Features:
- Responsive design for various devices (desktop, mobile, tablet)
- Offline access to course content
- Guided learning paths
- Adaptive learning and content recommendations
3. User management: Administrators can manage users (learners, instructors, and other staff) by creating accounts, assigning roles, and granting permissions. This feature enables the tracking of user progress and performance.
Features:
- Account creation, modification, and deletion
- Role assignment and permissions management
- Bulk user import and group management
- Password management and security options
4. Enrollment and registration: LMSs streamline the process of enrolling learners in courses and tracking their registration information.
Features:
- Course enrollment and waiting list management
- Registration details and tracking
- Automated notifications and reminders
- Self-enrollment options
5. Assessment and evaluation: The best LMSs offer built-in assessment tools, such as quizzes, tests, and assignments, to gauge learners’ understanding of the course material. Instructors can track learner progress and provide feedback on their performance.
Features:
- Built-in quizzes, tests, and assignments
- Automated grading for objective assessments
- Feedback tools for subjective assessments (essays, projects)
- Rubrics and scoring guidelines
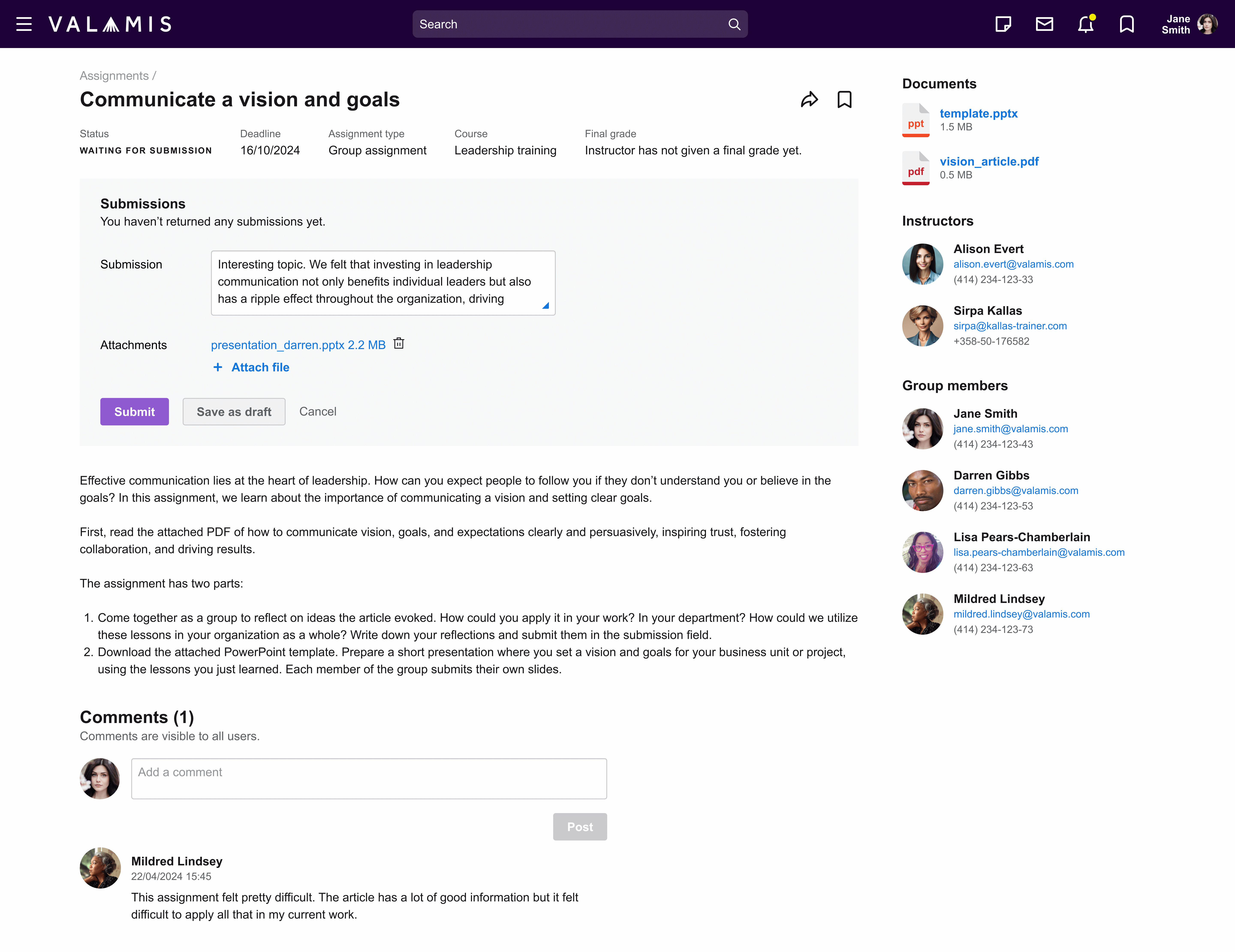
This is an example of the Valamis feature for course group assignment.
6. Communication and collaboration: LMSs facilitate communication between learners and instructors, as well as peer-to-peer interaction, through tools like discussion forums, messaging systems, and chat features.
Features:
- Discussion forums
- Messaging systems and chat features
- File sharing and collaboration tools
- Integration with video conferencing platforms
- Event management and scheduling capabilities
7. Tracking and reporting: LMSs track various aspects of learner progress, such as course completion, grades, and time spent on tasks. Administrators and instructors can generate reports to evaluate the effectiveness of the training programs and identify areas for improvement.
Features:
- Learner progress monitoring
- Customizable reports and analytics
- Experience API (Tin Can API)
- Data export options (CSV, Excel, PDF)
- Visualizations and dashboards
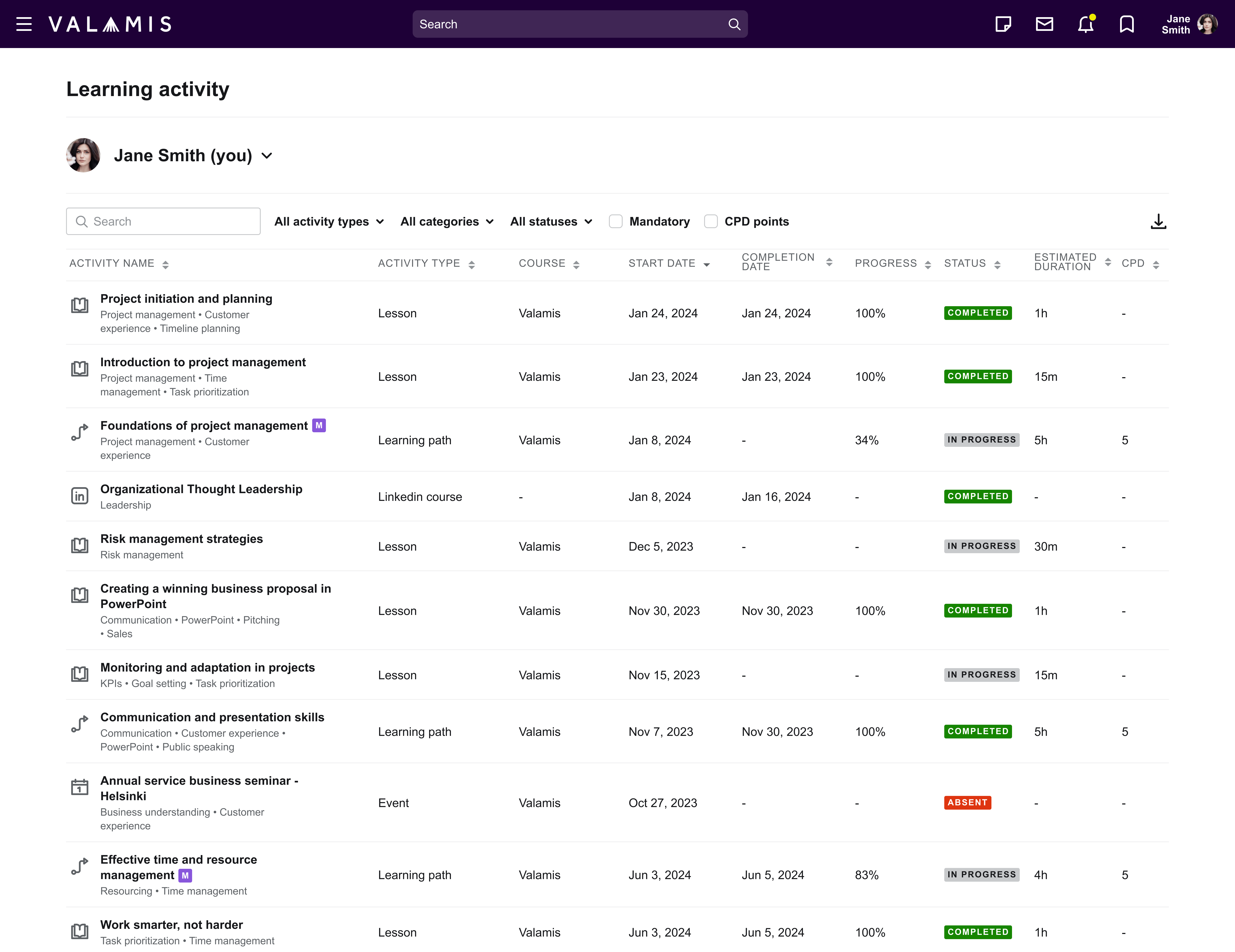
This is an example of one of the reports at Valamis.
8. Integration with other tools: LMSs can often integrate with third-party applications, such as video conferencing tools, content repositories, and CRM or HR systems, to enhance their functionality.
Features:
- Third-party tool integration
- API access for custom integrations and extensions
- Single sign-on (SSO) and authentication options
9. Customization and branding: Many LMSs allow organizations to customize the look and feel of the platform to match their branding and create a unique learning environment.
Features:
- Customizable themes and appearance
- Logo and branding elements
- Configurable navigation and menus
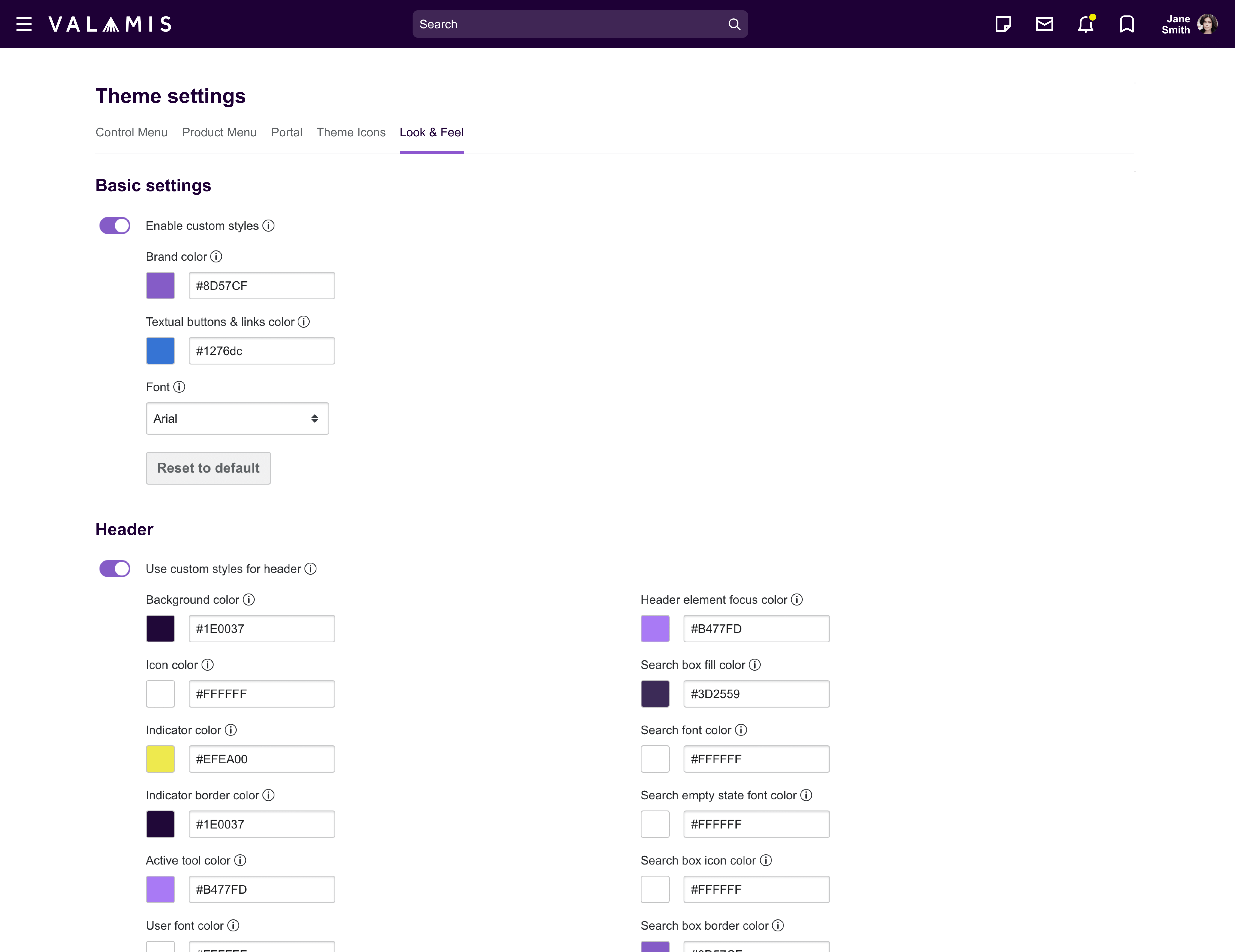
This is an example of Theme Editor at Valamis to customize the platform view to the final user
10. Mobile learning: Many LMSs are optimized for mobile devices, enabling learners to access course content and engage with their peers and instructors from smartphones and tablets.
Features:
- Responsive design for mobile devices
- Mobile app support (iOS, Android)
- Offline access to course content
11. Multi-language and accessibility: The ability to offer courses and interface elements in multiple languages.
Features:
- Multiple language support for courses and interface elements
- Compliance with accessibility standards
- Alternative content formats (audio descriptions, transcripts)
12. Security and data protection: Features to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of user data, including encryption, authentication, and backup options.
Features:
- Encryption and authentication
- Regular backups and data recovery options
- Compliance with data protection regulations (GDPR, FERPA)
This is not an exhaustive list of the many features that a LMS can offer your organization.

Checklist on how to choose the best LMS
The checklist will keep your focus on what really matters when choosing an LMS.
DownloadHow to find the right Learning Management System (LMS)
The value of choosing the right LMS cannot be overstated. According to a recent report from MarketsandMarkets, the LMS market size is projected to grow from USD 24.7 billion in 2022 to USD 52.7 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing recognition of LMSs as vital tools in both educational and corporate sectors.

However, with this rising prominence of LMSs has come a flood of options on the market, each offering a unique blend of features and functionalities. This makes the task of choosing an LMS that perfectly suits your needs a considerable challenge.
This is your guide to navigate the complexities of choosing the right learning management system, ensuring it aligns with your objectives, technological capabilities, and budget.
Step 1. Identify your organization’s learning needs
The first step to choosing an LMS is understanding what you want from your L&D program. Without a goal, you won’t know what to look for.
So, what are your business objectives? And how could a new approach to employee training support them? These two questions define your organization’s learning needs.
Look at the Johanna’s example of 5 why’s of corporate training for manufacture company below. Use this technique of 5 why’s when a problem occurs or when you need to understand the real goals. You drill down to its root cause by asking “Why?” five times.
The example of 5 why’s of corporate training for manufacture company
- Why do companies have training programs? – for onboarding, compliance (security, regulations, etc.), and product and service training. So, to deliver company-specific training.
- Why the need to deliver company-specific training? – job-related tasks, reduce employee turnover, talent attraction, and talent retention. So, to focus on talent.
- Why the focus on talent?– enhance employee experience, and increase productivity and efficiency at work. So, to focus on EX, productivity, and efficiency.
- Why the focus on focus on EX, productivity, and efficiency? – build business resilience and improve business performance. So, to focus on business reliance and performance.
- Why the focus on business reliance and performance? – Stay relevant in the industry.
You can read other Johanna’s article on How to Create an Effective L&D Strategy
Step 2. Define your criteria for selecting an LMS
With these needs in mind, you can define your criteria for selecting an LMS, breaking down requirements into the LMS functionality to help meet your goals. However, this is not a simple task, and there is lots to consider.
For example, what types of content will be most effective for your employees?
Do you need a platform that supports new learning scenarios such as microlearning, gamification, or social learning?
Other factors to examine include ease of use, customization options, content library, reporting and analytics, integrations, scalability, and more.
You may also want to consider the vendor’s reputation, customer support, and pricing model.
Step 3. Assess your budget
In a perfect world, you could design a perfect, bespoke LMS that does everything you could think of and more. In reality, you will have to operate under budgetary constraints.
Remember to include the total cost of ownership for the new system, including implementation, licensing fees, maintenance, support, and any additional costs like customizations or integrations.
But also remember to consider the other side of the equation – the potential long-term savings on offer through improved efficiency and productivity.
Additional reading: How to Connect Learning Data to Your Business Success
Step 4. Gather stakeholder input
A new LMS’s success depends on many stakeholders, including administrators, instructors, and learners.
Therefore, expanding the number of people with input into the decision is critical, ensuring the selected LMS results in a positive experience for everyone interacting with it.
Involve stakeholders from different departments in the selection process to get a diverse range of opinions to ensure your chosen solution will meet the needs of everyone.
Collect their feedback on desired features, potential challenges, and specific needs.
Step 5. Create a feature checklist
After defining your goals and hearing from key stakeholders, you can build a checklist of essential LMS features. Prioritize based on relative importance and relevance to your overall e-learning strategy. Creating a feature checklist provides a valuable reference to evaluate the various LMS options.
Step 6. Research and shortlist vendors
Conduct market research to identify LMS vendors with solutions aligned with your requirements. Compare their products, features, pricing, and reputation.
Shortlist the vendors that best meet your needs and budget for further research.

Step 7. Request for information (RFI)
Once you have a shortlist of possible vendors, you should create a Request for Information (RFI) to delve deeper into their products.
An RFI includes a series of questions to determine if a solution fits your organization and its needs. See the next section for examples of the questions to ask in an RFI.
Step 8. Evaluate shortlisted LMS solutions
Evaluate your shortlist of potential LMS solutions based on returned RFIs and your feature checklist. Involve stakeholders in the process and collect their feedback to ensure the chosen LMS meets everyone’s needs. For example, you don’t want to focus on the opinion of administrators at the expense of the learner’s experience.
At the evaluation stage, you can also request demos or trial access to your shortlisted LMS solutions to better understand how the software works in practice. This includes the user interface, navigation, features, and customization options. Again, invite stakeholders also to review the software and provide feedback.
Step 9. Investigate integration and compatibility
Assess how the LMS would integrate with the HR systems already in use at your organization.
Check that the LMS supports compatible industry standards to ensure seamless operations across the various tools and platforms.
Step 10. Review security and Data Privacy
Confirm that the LMS adheres to necessary industry standards for data privacy and complies with relevant regulations like GDPR or FERPA.
Review how the vendor handles data and the policies they have in place, including encryption methods and security certifications.
Step 11. Check support and training
Discuss and verify with previous client testimonials the level of support the LMS vendor offers.
Consider the availability of a dedicated account manager or support team capable of assisting with implementation, troubleshooting, and ongoing maintenance.
Step 12. Make a final decision and get started
After a thorough evaluation, select the LMS that best meets your organization’s needs, objectives, and budget. Work closely with the vendor to plan and execute a smooth implementation process. Train relevant stakeholders to use the new platform and continuously monitor its effectiveness to ensure it delivers on your e-learning goals.

Checklist on how to choose the best LMS
The checklist will keep your focus on what really matters when choosing an LMS.
DownloadNext steps:
- If you are unsure about whether you are ready to invest in an LMS, check out our comprehensive checklist on Assessing Readiness for Corporate Learning Solutions.
- If you are in the process of selecting the right vendor, you can download an RFP template for this purpose.
- If you are seeking a reliable partner in learning, explore what Valamis can offer you.




